
 0 reactions
0 reactions
In PySpark, DataFrames are the primary data structure used for working with structured data. They provide a convenient interface for performing various operations on data, similar to DataFrames in pandas or SQL tables.
This article serves as a comprehensive cheat sheet for various DataFrame operations in PySpark. It covers essential operations such as data loading, manipulation, filtering, aggregation, joining, and more. Each section provides code examples along with explanations to help you understand and apply these operations effectively in your PySpark projects.
Using withColumn, we can add new column to the existing dataframe. This will create and return new dataframe
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import when, col
# Initialize SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Add Column") \
.getOrCreate()
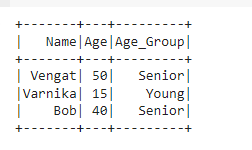
data = [("Vengat", 50), ("Varnika", 15), ("Bob", 40)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Name", "Age"])
# Add a new column based on an existing column
df_with_new_column = df.withColumn("Age_Group",
when(col("Age") > 35, "Senior")
.otherwise("Young"))
# Show the updated DataFrame
df_with_new_column.show()
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
# Initialize SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Modify Column Example") \
.getOrCreate()
# Sample DataFrame
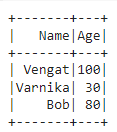
data = [("Vengat", 50), ("Varnika", 15), ("Bob", 40)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Name", "Age"])
# Modify the "Age" column by multiplying each value by 2
df_modified = df.withColumn("Age", col("Age") * 2)
# Show the modified DataFrame
df_modified.show()
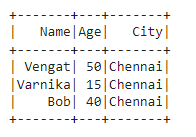
A constant column to a DataFrame in PySpark involves using the withColumn() function along with the lit() function to specify the constant value. Here's how you can do it:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import lit
# Initialize SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Add Column") \
.getOrCreate()
data = [("Vengat", 50), ("Varnika", 15), ("Bob", 40)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Name", "Age"])
# Add a constant column named "City" with value "Chennai"
df_with_city = df.withColumn("City", lit("Chennai"))
# Show the updated DataFrame
df_with_city.show()
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import concat, lit
# Initialize SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Concatenate Columns") \
.getOrCreate()
# Sample DataFrame with Indian names
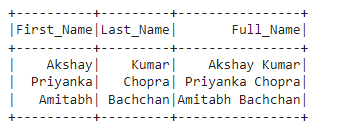
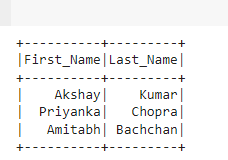
data = [("Akshay", "Kumar"), ("Priyanka", "Chopra"), ("Amitabh", "Bachchan")]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["First_Name", "Last_Name"])
# Concatenate "First_Name" and "Last_Name" columns into a new column "Full_Name"
df_with_full_name = df.withColumn("Full_Name", concat(df["First_Name"], lit(" "), df["Last_Name"]))
# Show the DataFrame with the concatenated column
df_with_full_name.show()
new_df = df_with_full_name.drop("Full_Name")
# Rename the column "Name" to "Full_Name"
df_renamed = df.withColumnRenamed("Name", "Full_Name")
# Show the DataFrame with the renamed column
df_renamed.show()
# Sample DataFrame
data = [("John", 30, "Male"), ("Jane", 35, "Female"), ("Bob", 40, "Male")]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Name", "Age", "Gender"])
# Define the mapping of old column names to new column names
column_mapping = {
"Name": "Full_Name",
"Age": "Years",
"Gender": "Sex"
}
# Rename the columns using a loop
for old_name, new_name in column_mapping.items():
df = df.withColumnRenamed(old_name, new_name)
# Show the DataFrame with the renamed columns
df.show()
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Initialize SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Convert Column to List Example") \
.getOrCreate()
# Sample DataFrame
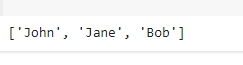
data = [("John", 30), ("Jane", 35), ("Bob", 40)]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["Name", "Age"])
# Select the column you want to convert to a list and collect the values into a list
name_list = df.select("Name").rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x).collect()
# Show the Python list
print(name_list)
df_filtered = df.filter(df["Age"] > 30)
# Sort rows by Name in descending order df_sorted = df.orderBy(df["Name"].desc())
df_grouped = df.groupBy("Name").agg({"Age": "avg"})
# Join two DataFrames df1 and df2 on the common column "ID" df_joined = df1.join(df2, df1["ID"] == df2["ID"], "inner")
df_pivoted = df.groupBy("Col1").pivot("Col2").agg(F.sum("Value"))
from pyspark.sql.window import Window
import pyspark.sql.functions as F
window_spec = Window.partitionBy("Department").orderBy("Salary")
df.withColumn("rank", F.rank().over(window_spec))
from pyspark.sql.functions import udf
from pyspark.sql.types import StringType
# Define UDF to convert names to uppercase
upper_udf = udf(lambda x: x.upper(), StringType())
# Apply UDF to DataFrame column "Name"
df_with_upper_name = df.withColumn("UpperName", upper_udf(df["Name"]))
df_distinct = df.select("Name", "City").distinct()
df_no_duplicates = df.dropDuplicates(["Column1", "Column2"])
df_filled = df.fillna(0) # Fill null values with a specific value
df_converted = df.withColumn("NewCol", df["OldCol"].cast("double"))
 0 reactions
0 reactions